Insulation resistance monitoring as a requirement for safe use of electricity grids
Insulation resistance is a parameter that characterises an electricity grid, and one of the most important criteria in evaluating its quality and safety in use. Controlling insulation condition is a legal requirement, and it includes periodic installation control in buildings.
Insulation resistance measurement provides information about the condition of a dielectric that separates live wires from one another and from the ground, both in electric devices and grids.
When the received results are correct?
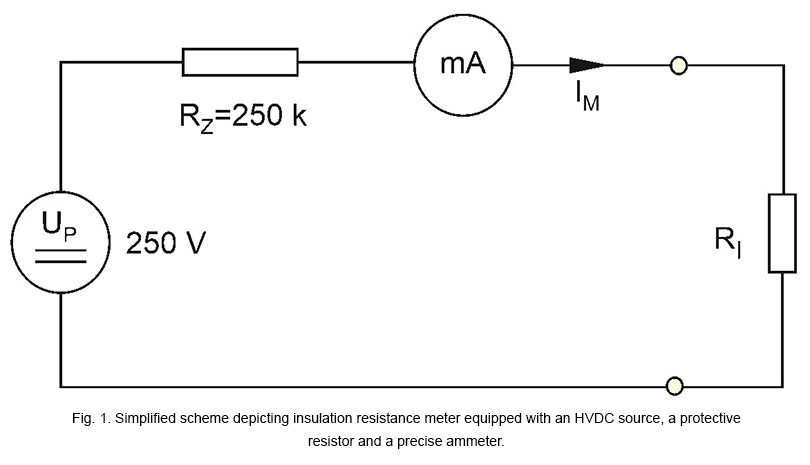 A regular ohmmeter is not enough to measure insulation resistance. A specialist meter has to be used, as the majority of measurements require a high measurement voltage (250V-2.5kV) to be sent to the circuit, not just a few Volts, as in the case of multimeters. Measurement ranges of up to 20 GΩ are necessary (fig. 1).
A regular ohmmeter is not enough to measure insulation resistance. A specialist meter has to be used, as the majority of measurements require a high measurement voltage (250V-2.5kV) to be sent to the circuit, not just a few Volts, as in the case of multimeters. Measurement ranges of up to 20 GΩ are necessary (fig. 1).
What comprises the measurement component system?
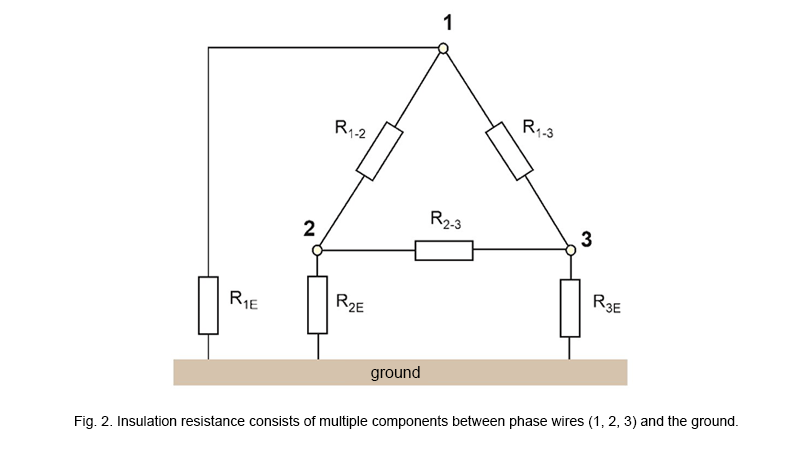 Insulation resistance is not only the measurement of resistance between two wires of a cable. It’s also the surface resistivity of an insulator that depends on the purity of the surface. Apart from the resistance between two wires of a cable, the resistance between each wire and the ground is important as well.
Insulation resistance is not only the measurement of resistance between two wires of a cable. It’s also the surface resistivity of an insulator that depends on the purity of the surface. Apart from the resistance between two wires of a cable, the resistance between each wire and the ground is important as well.
This forms the complex measurement component system (fig. 2).At high grid voltage we have to take into account additional phenomena that occur in dielectrics, which are caused by orientation of the electric charges inside the insulation material along the electric field lines.
What measurement capabilities do insulation resistance meters offer?
Specialist insulation resistance meter enables you to conduct measurements in accordance with applicable standards, i.e. for specified measurement voltage and with appropriate precision.
It enables:
- voltage adjustment,
- measurement time adjustment,
- recurrent measurements,
- leakance measurements,
- dielectric polarization current measurements.
Advanced instruments allow for measurements with the use of the 3-wire method, thanks to which the impact of leakance on the actual results can be eliminated.
Summary
Insulation resistance measurement enables detection of invisible cable and installation damages caused by mechanical factors, humidity or dirt. By conducting measurements in various temperatures and humidity, you can also evaluate the condition and quality of the insulation of a particular cable.













